Here, we show two ways to establish a connection with the Oracle Database from a Windows computer.
You need to be connected to the Oracle instance you wish to monitor and run the Create Oracle user script.
CMD (SQL*Plus)
Connect to SQL*Plus through CMD (Windows Command Prompt). You must use the credentials of a SYS Oracle user (or equivalent).
- If you are logged in with a Windows user that already has SYS privileges, run the following command on the CMD.
sqlplus / as sysdba- Else, run the following command, changing “adminpass”, “hostname”, “port”, and “servicename” with the proper parameters of a SYS Oracle user.
sqlplus sys/adminpass@hostname:port/servicename as sysdbaNotice:
- When running a script through the CMD (SQL*Plus) interface, each paragraph of the script should be run one at a time.
- To check the Oracle instance you are connected to, run the following command
select open_mode, name from v$database /- If you are not connected to the correct Oracle instance, run the following commands, one at a time, where the “servicename” is the name of the Oracle instance you want to connect to:
quitset ORACLE_SID=servicenameOracle SQL Developer
- In Windows Search, look for “SQL Developer” and open it
- Search for connections, click on the green plus (+), and create a new ORACLE connection with the SYSDBA privileges login details:
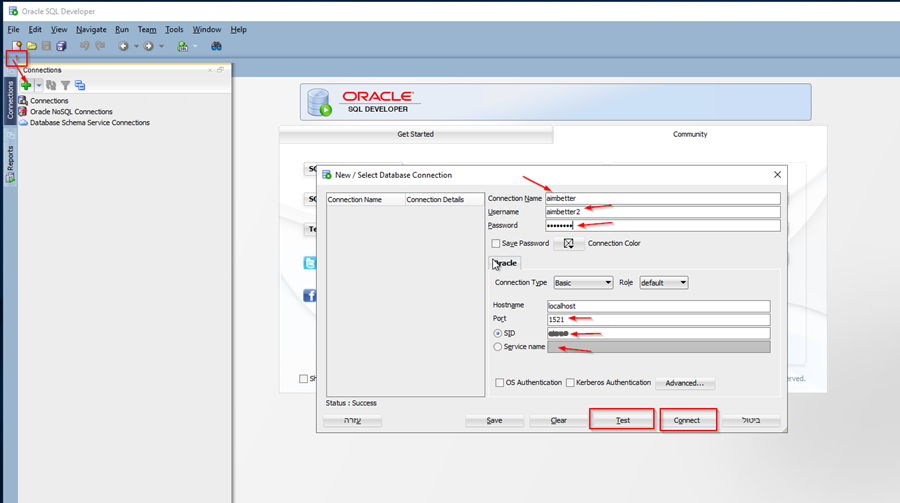
- Details:
- Connection name – Display the name of the connection
- Username – Username
- Password – Password
- Host Name- If you log in locally to SQL Developer at the Oracle Host Server, the hostname remains the same (‘localhost’).
- Port – fill in the port number (default is 1521)
- SID/Service Name – Choose one of them and enter the Instance name.
Click on test and look for the “Success” message.
If the Success message is displayed, click on Connect.

 +1 (650) 449-8622
+1 (650) 449-8622